Personalised Learning
Personalised learning is a flexible, people focussed framework that places the participant at the center of their educational experience. This approach attempts to nurture autonomy, engagement, and meaningful progress of all involved. Importantly, personalised learning approach ensures that every learning journey as unique and impactful as the individual perusing it. Expanding on its foundational concepts, personalised learning can be understood through six interconnected pillars that guide facilitators in creating dynamic, participant-driven environments.
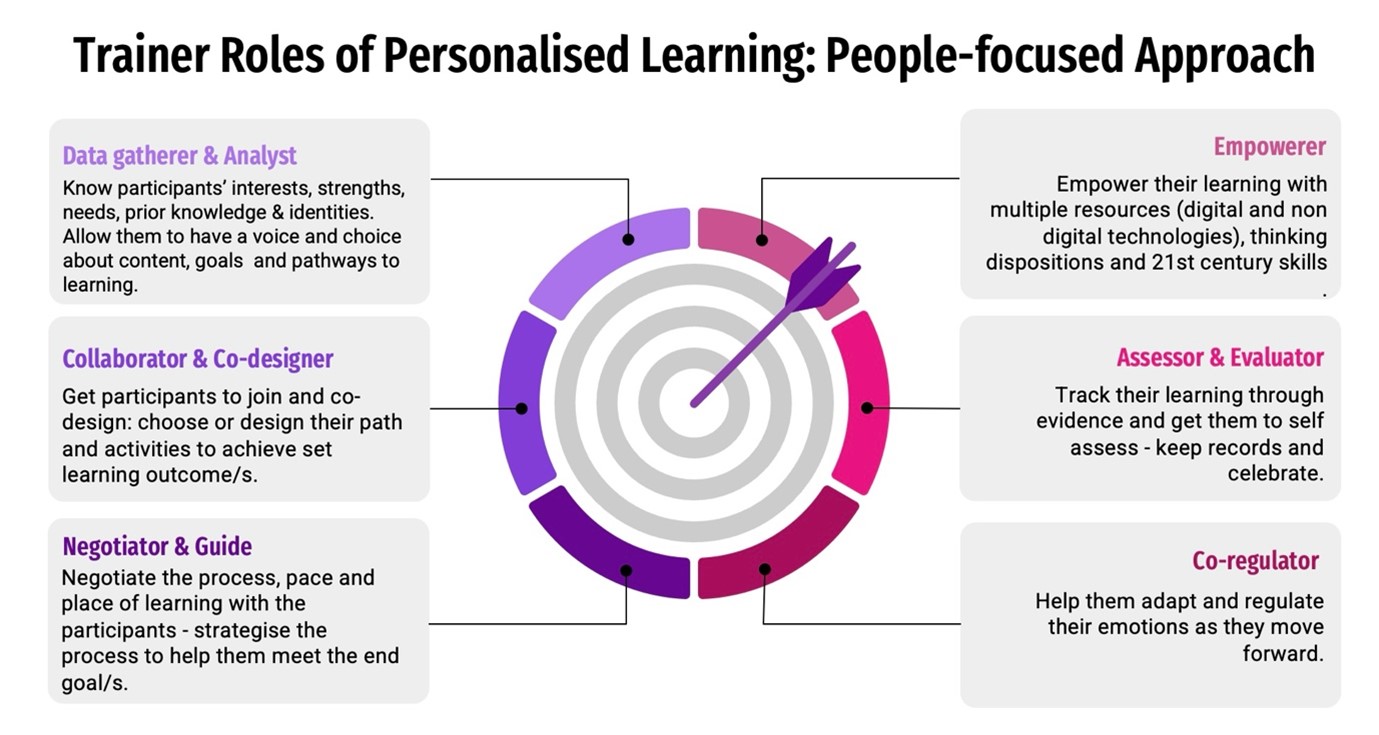
1. Understanding learners and developing their learner identities
Personalised learning begins with uncovering the participants’ unique characteristics, which involves understanding their existing knowledge, strengths, and interests. Facilitators take on the role of gathering this insight acting as data gatherers and analysts, ensuring that learning is rooted in their individual context, promoting engagement and ownership.
2. Collaborating and designing learning experiences together
Participants are not merely passive recipients of content, but play an active role in crafting their educational pathways. Facilitators work alongside them and act as collaborators and co-designers by co-creating meaningful activities that align with the set learning goals. With those shared-responsibility model.
3. Negotiating and guiding the learning process
Facilitators play a critical role as supportive negotiators and guides working with participants to refine their learning strategies. It involves adapting the pace and methods of learning to suit the needs of individuals while maintaining a focus on the desired outcomes. Through regular reflection and discussion with the participants, facilitators empower the participants to feel confident in adapting their journey to overcome challenges.
4. Empowering learners with tools and resources
Facilitators act as empowerers, providing access to diverse resources – both digital and non-digital, as well as fostering thinking dispositions and 21st-century skills like creativity, critical
thinking, and collaboration. By incorporating such approaches, facilitators enable participants to navigate their learning in ways that feel relevant and enriching.
5. Assessing and evaluating competency-based growth
Assessment in personalized learning goes beyond measuring outcomes—it involves tracking progress in meaningful ways. Facilitators act as assessors and evaluators, whereby the learning is evaluated not as a final judgment, but as an ongoing process that emphasises the growth of participants. Competency-based assessment provides participants to demonstrate mastery through varied means, making evaluation more inclusive, equitable, and aligned with individual learning journeys.
6. Supporting emotional and behavioural resilience
Learning is seen as an emotional journey as much as an intellectual one. Facilitators serve as co-regulators, helping the participants adapt to challenges, to handle setbacks by cultivating emotional resilience. By offering consistent support, facilitators help participants navigate the complexities of the learning process with confidence and determination. They help their participants to have clear goals, monitor learning, analyse tasks, understand expectations and use strategy, monitor learning and reflect on the learning process.
Exploring the Complexity of Personalised Learning
Personalised learning has gained traction as a powerful approach to tailoring eucation to individual student needs, strengths, and interests. While teachers agree with its theoretical clarity, this study highlights the significant challenges they face in practical implementation. From sustaining student engagement to balancing curriculum demands, the findings reveal a nuanced picture of personalised learning in action
Read more: The simple, the complicated, the complex and Chaotic